 今天是个好天气
今天是个好天气
 今天是个好天气
今天是个好天气
 今天是个好天气
今天是个好天气
Redis是内存存储的,以键值对形式,存在内存当中。
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
// 数据库键空间,保存着数据库中的所有键值对
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
// 键的过期时间,字典的键为键,字典的值为过期事件 UNIX 时间戳
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
// 正处于阻塞状态的键
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP) */
// 可以解除阻塞的键
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
// 正在被 WATCH 命令监视的键
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
struct evictionPoolEntry *eviction_pool; /* Eviction pool of keys */
// 数据库号码
int id; /* Database ID */
// 数据库的键的平均 TTL ,统计信息
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
} redisDb;
Redis的存储是字典结构,set a b之后,a会放在字典的对应偏移位置,b作为对应的value进行存储。
存放在expire当中,一旦设置就加入。
set hellomsg "hello world"
get hellomsg
del hellomsg
Redis数据可以设置过期键,到时间后自动过期回收,过期键存放在expires字典上。
一旦设置了过期键,立马加入expires当中,查询数据时先去expire字典上判断是否过期,过期就不返回。
在dict和expires中Key对象都是存储String对象指针,不会重复占用内容。
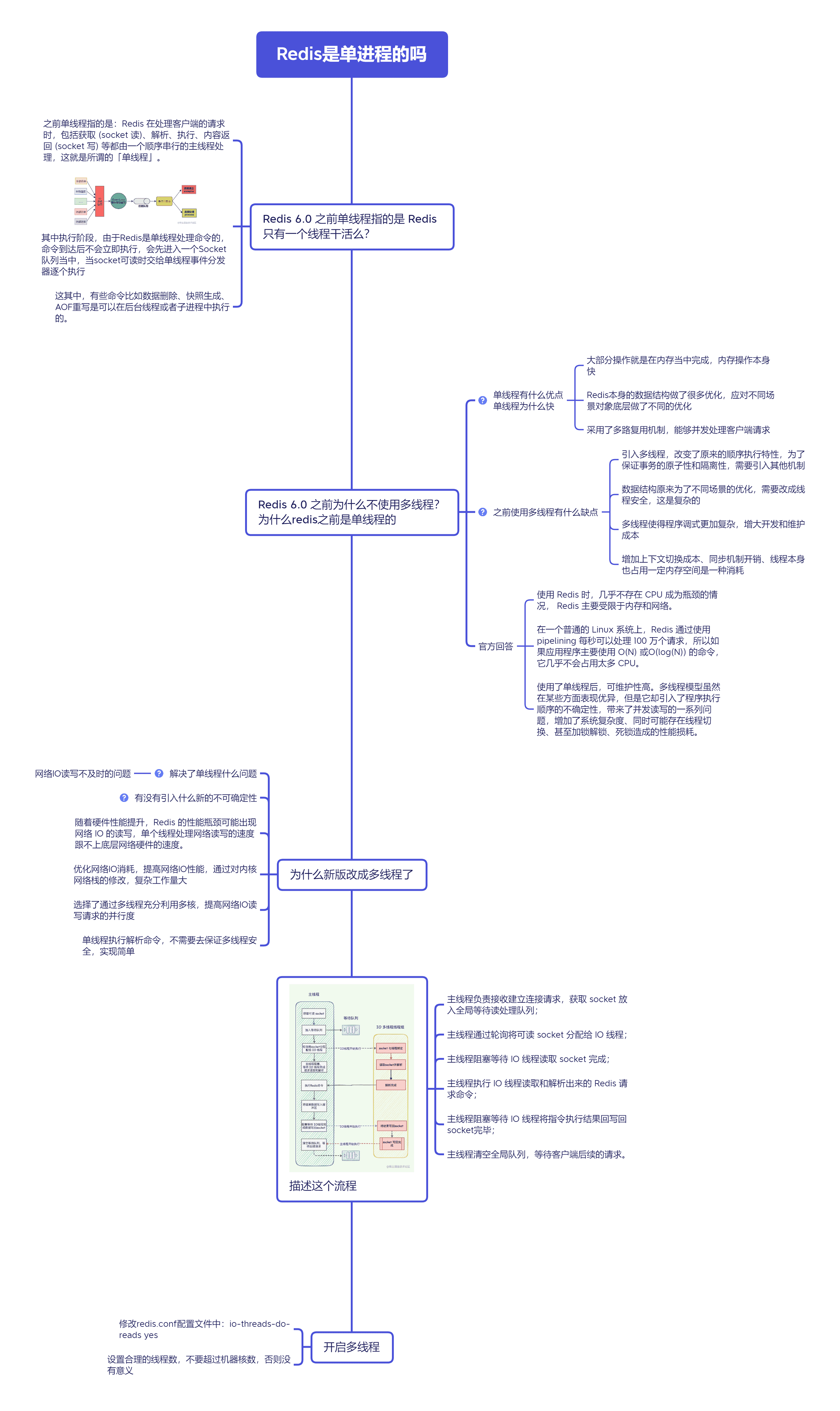
https://www.luozhiyun.com/archives/674
Redis是基于内存存储的,在64位机器默认不会限制内存的使用,在 32 位操作系统中,maxmemory 的默认值是 3G。
实际中通过maxmemory来设置,超过这个配置值,会触发Redis内存淘汰。
当内存不足时,会腾出部分内存给新数据,因此Redis支持多种淘汰策略:
不进行数据淘汰的策略,默认是noeviction,如果内存达到了maxmemory,写入操作会失败,但是不会淘汰已有的数据。
针对「进行数据淘汰」这一类策略,又可以细分为「在设置了过期时间的数据中进行淘汰」和「在所有数据范围内进行淘汰」这两类策略。
在设置了过期时间的数据中进行淘汰:
在所有数据范围内进行淘汰:
实际当中根据业务选择淘汰算法:
淘汰时机:
每次运行读写命令时,都会调用processCommand函数,其又会调用freeMemoryIfNeed,这时候会尝试去释放一定的内存,根据上述的策略。